Introduction
Robotic surgery has revolutionized the field of healthcare, offering numerous benefits, such as reduced pain, smaller incisions, faster recovery times, and improved precision. However, the adoption of this cutting-edge technology also raises ethical concerns that need to be addressed to ensure responsible and ethical use of robotic surgery. In this article, we will explore the ethical implications of robotic surgery in healthcare, examining its potential benefits, risks, and the ethical principles that guide its use.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery has ushered in a new era of medical possibilities, providing numerous advantages to both patients and healthcare providers. The key benefits include:
Enhanced Precision: By utilizing advanced robotic systems, surgeons can perform procedures with unmatched precision and accuracy, reducing the risk of errors.
Reduced Pain and Smaller Incisions: Robotic surgery often results in smaller incisions, which lead to reduced pain and discomfort for patients during the post-operative period.
Faster Recovery Times: Patients experience shorter recovery times compared to traditional surgery, allowing them to return to their daily lives sooner. Robots can make more precise and controlled incisions, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. This precision reduces trauma to the body, resulting in less pain and faster healing.
Less Scarring and Improved Cosmetics: Smaller incisions result in less scarring and better cosmetic outcomes for patients.
Increased Range of Motion for Surgeons: Surgeons can perform complex maneuvers with greater ease using robotic systems.
Reduced Risk of Infection: The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery reduces the risk of post-operative infections.
Improved Visualization: Surgeons benefit from enhanced visualization of the surgical site, leading to better decision-making during the procedure.
Shorter Hospital Stays: Shorter recovery periods mean reduced hospital stays, ultimately lowering healthcare costs for both patients and institutions.
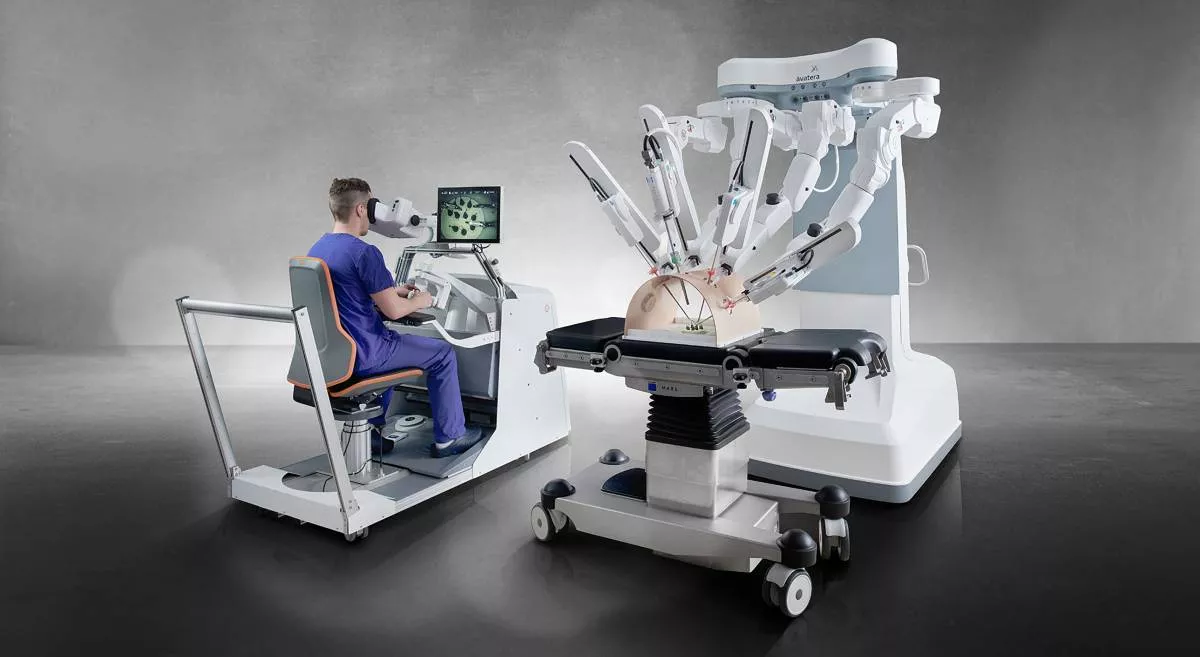
Risks Associated with Robotic Surgery
While the benefits of robotic surgery are significant, there are associated risks and challenges that need to be considered:
Complications During Surgery: As with any surgical procedure, complications like bleeding, infection, and organ damage can occur.
Technical Malfunctions: Surgical robots may experience technical malfunctions, such as instrument failure or communication issues, which could jeopardize patient safety.
Surgeon Inexperience: Inexperience with robotic surgery among some surgeons may increase the likelihood of errors during procedures, highlighting the importance of proper training.
Access Barriers: The cost of robotic surgery can be a barrier to access for patients who cannot afford it. Ethical concerns include ensuring that healthcare remains accessible to all.
Patient Safety and Informed Consent: Patient safety should be the top priority, and surgeons must obtain informed consent, providing comprehensive information about the potential risks and benefits of robotic surgery.
Ethical Implications of Robotic Surgery
The ethical implications of robotic surgery in healthcare are multifaceted and require careful consideration:
Patient Safety: The primary ethical concern is ensuring patient safety. Surgeons must undergo specialized training, be certified to perform robotic procedures, and continually monitor the surgical event for mechanical dysfunction.
Professional Ethics: Surgeons and healthcare professionals involved in robotic surgery must adhere to ethical principles, including informed consent, privacy, and confidentiality.
Transparency: Transparency is vital in establishing trust between surgeons and patients. Patients should receive clear and accurate information about the surgeon’s experience with robotic surgery, as well as the costs, benefits, and potential risks associated with the procedure.
Innovation: Innovation in robotic surgery brings new challenges and unknown risks. Continuous evaluation and improvement are necessary to ensure the ethical use of this technology.
Surgical Outcomes: Robotic surgery should be evaluated based on patient outcomes, including the reduction of complications, pain, length of hospital stay, and overall recovery time.
Conflicts of Interest: Healthcare providers must ensure that financial considerations do not influence decisions regarding the use of robotic surgery. Patients should be informed about any financial interests the surgeon or hospital may have in promoting robotic surgery.
Regulation: Currently, there is limited regulation of robotic surgery. Regulatory bodies must establish guidelines to ensure the responsible and safe use of robotic surgery in healthcare.
Training and Education: Surgeons require specialized training and education to become proficient in robotic surgery. Ongoing training and education are vital to maintain ethical practice and deliver optimal patient care.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery has transformed the field of healthcare, offering numerous benefits to patients and healthcare providers. However, the adoption of this technology also raises ethical concerns that must be addressed. As medical technology continues to advance, it is imperative to thoroughly analyze the ethical implications of emerging innovations like robotic surgery. This will enable us to harness the benefits of these technologies while upholding the highest standards of ethical medical practice.
